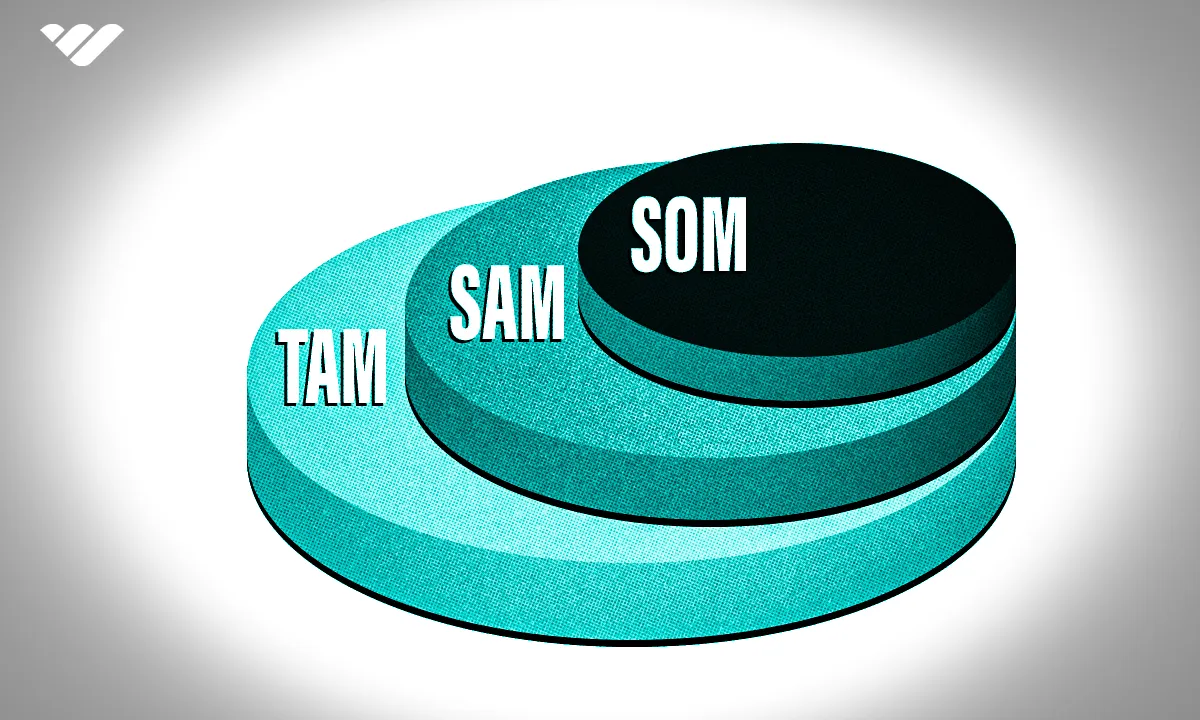
TAM (Total Addressable Market), SAM (Serviceable Addressable Market), and SOM (Serviceable Obtainable Market) measure your market size at three levels. Learn how to calculate each metric in 5 steps with real business examples in this guide.
Key takeaways
- TAM, SAM, and SOM help you progressively narrow market size from total opportunity to realistic revenue goals.
- Bottom-up TAM calculation using your actual customer data provides more accurate estimates than top-down industry research.
- SOM represents your achievable short-term revenue target based on competition and previous market share performance.
You can calculate your market size in 5 steps:
- Figure out your target market
- Use TAM to find your Total Addressable Market
- Use SAM to refine to the Serviceable Market for your product
- Use SOM to discover Your Potential market share
- Outline your opportunities and challenges
One of the main things you’ll consider throughout your business’ lifetime is its market. When starting a business, you must understand if there’s a market for your product. And, when your product or services are doing well, you’ll need to find ways to pivot and expand them to grab a larger market share.
There are many metrics that will help you with this, but one of the main ones is TAM SAM SOM. No, this isn’t some kind of encrypted code or letters put together randomly.
Rather, it’s a tool that you can use to find the total market your product speaks to, the part of the market that you can realistically address, and the small slice of it that you obtain.
We’ll cover everything you need to know about TAM SAM SOM below and go over some examples so that you can start utilizing the metrics in your business strategy.
TAM SAM SOM: Meanings, calculations, and examples
First off, we have to explain what the acronyms mean and how you can calculate them using data from your market and business.
TAM (Total Addressable Market)
TAM stands for Total Addressable Market. It’s the maximum demand for your product/service if it caters to every customer and if we remove all competition from the equation.
Essentially, TAM is your total potential revenue if you have no competitors and your products or services cover all of your customers' needs. As you can imagine, catering to the entire TAM is impossible, as there will always be competitors who will take a slice of the pie, regardless of how complete your offering is.
How to calculate TAM
Its definition might be rather simple, but calculating TAM can be quite challenging. There are 2 main methods businesses use to calculate TAM: top-down and bottom-up.
- Top Down Calculation: Total Industry Annual Revenue x Market Segment % x Penetration Rate
With this approach, you have to scour the internet for data regarding your market. You’ll need to find the total amount of revenue in your industry.
Then, you can use demographic data to narrow the sector to your specific market. All that’s left is multiplying with the expected penetration rate (how many potential customers actually buy something).
For instance, if the total annual revenue of your industry is at $10 billion with a penetration rate of 20%, and your market segment is at 10%, then your TAM would be $200 million.
As you can see, this isn’t the most accurate method. Much of this data might be outdated or inaccurate. So, instead of doing that, you can opt for the bottom-up approach.
- Bottom Up Calculation: Total Market x Annual Revenue Per Customer
With bottom-up, you calculate your TAM by utilizing your current revenue per customer and the number of potential customers.
Considering that you’ve already had some sales, simply divide your revenue by the number of customers you have and multiply that number by the total potential customers.
In business terms, you need the total market and the ACV (Annual Contract Value), ARPU (Average Revenue Per User), or whatever other acronym you use to determine the average annual revenue per customer.
For example, if you sell products at $500-$1000 and have 10 customers with total revenue at $15000, your ARPU (or ARPC in this case) is $1500. In a market where you can address 10 million customers, your TAM would be $15 billion.
Now, what if you haven’t had a sale yet or are pivoting to an entirely different product/service? The calculation is pretty much the same. Instead of using actual numbers, you’ll use estimates based on your competitors.
So, if your main competitors sell a new product at $200, with potential customer numbers being at 20 million, your TAM is $4 billion. Or, if you believe that you can sell your product at a 10% premium because it has a better feature, your TAM is $4.4 billion.
SAM (Serviceable Addressable Market)
SAM stands for Serviceable Addressable Market. It’s the ideal number of customers (or percentage of TAM) you can realistically service as your business grows.
Think of SAM as a sub-niche. It’s your slice of the pie (with the pie being TAM, in this case). When you, for example, sell access to a community, your TAM is all potential community members, while your SAM is only the ones who use Whop, Discord, Telegram, or any other specific platform where you’ll host your community.
How to Calculate SAM
Target % of Total Market x Annual Revenue Per Customer or Target % of TAM
Calculating SAM is a bit more simple than TAM, but of course, you have to get TAM before you can calculate SAM. Once you have that, find the percentage of TAM that you wish to target and multiply it by the ARPC. We’ll have to use some hypotheticals here.
So, let’s say that you’re selling courses exclusively to US customers, with an ARPC of $100 and a total market of 10 million potential users (so, a $1 billion TAM). But, your course is designed for males in the 18-24 age range, which accounts for 5% of your TAM.
Thus, the SAM would be 5% of $1 billion, which comes out to $50 million. You’ll also find the same SAM if you consider that since your audience is 5% of the total market (so, 500,000 in total), and the ARPC is $100.
SOM (Serviceable Obtainable Market)
SOM stands for Serviceable Obtainable Market. It’s the actual number of customers (or percentage of SAM) you service (or can service if you don’t have any sales yet) based on the amount of competition.
SOM is basically your short-term revenue goal. Ideally, your SOM should be as large of a percentage of SAM as possible, but that depends on how much competition your market has.
Let’s say you sell access to a whop, and your SAM is the total number of folks buying memberships on Whop. You’re going up against, say, 99 whops with similar products or services. A reasonable SOM would be 1% of the SAM. So, with a SAM of, say, $50 million, your SOM is $500,000.
How to Calculate SOM
Previous Year's Market Share x Current Year's SAM
To calculate SOM, you’ll have to find your market share of the previous year, which you can do by dividing the SOM by the SAM. Then, you just multiply that by the current year’s SAM, and you’ve got your SOM for the year.
Let’s use the example we mentioned above. You’re selling courses with a SAM of $50 million, and you had a SOM of $1 million last year. So, your market share was 2%. This year’s projections are that SAM will increase by 10%, going up to $55 million. Thus, your SOM is 2% of $55 million, or $1.1 million. You can also say that since SAM is increased by 10%, your SOM has the same 10% increase.
TAM SAM SOM Examples
While we’ve gone over some examples, let’s set a few more in-depth ones. Let’s say you sell digital products (ebooks, in this case) or physical products (luxury watches, for example).
So, let’s start off with the digital side of things. You’ve written a Sci-Fi ebook you want to sell to a US audience through Amazon. According to reports, there were around 69 million ebook readers in the US last year. Let’s say that Amazon self-published ebooks account for 40% of the market, bringing a total market of 27.6 million readers.
Also, Sci-Fi ebooks take up 1% of that share, so your actual total market is 276,000 readers. Now, each reader spends an average of $75 on ebooks, so your TAM is $20.7 million.
Here’s where it gets a bit complex. You want to target a male audience in the 18-35 age range, which, for number’s sake, takes up 10% of the market. This won’t affect your TAM, as your ebook might also be read by other-gendered readers or ones that are outside of the age range. So, the SAM is going to be 10% of the TAM, or $2.07 million.
Now, the Sci-Fi space isn’t that competitive, hence why there are only, say 9 authors with equally-distributed market shares. And so, your market share last year would be 10%.
Finally, if we consider that the SAM will increase by 1% year-over-year ($2.09 million for this year), that brings your SOM to 10% of $2.09 million, or $209,000.
Confusing? Time to try another. Let’s quickly go over the luxury watch example. You’re launching a luxury watch business in Florida, with the state having a $1 billion annual revenue last year. Your TAM would, therefore, be $1 billion, as we’ve already narrowed this down a bit (specific state and market segment within the watch industry).
Now, if you’re primarily selling men’s watches, which take up 60% of sales, it means that your SAM is $600 million. That said, you’re going up against 99 male luxury watch dealers, but you have more premium selections, which increases your market share to 2%. This year, the market is estimated to increase by 5%, bringing the SAM up to $630 million. And, with a 2% market share, that brings this year’s SOM to $12.6 million.
How to calculate TAM SAM SOM for your business in 5 steps

We’ve seen examples of different businesses, but how can you calculate the TAM SAM SOM for your business? Let’s go over every step you’ll need to take, from beginning to end. We’ll also reiterate the course example (with some sample numbers) we mentioned above to make these steps as clear as possible.
1. Figure out your target market
Finding your target market is basically 90% of the work to find your TAM SAM SOM. Narrow this down as much as possible without excluding potential demographics that you can reach out to.
To figure out your target market, you should consider your potential audience:
- Location
- Age
- Gender
- Unique Traits
- Problems they want to solve
For example, let’s say that the online learning market sits at 1 billion users. Out of these, 100 million are in the US, of which 10 million are male in the 18-35 age range. 1 million of these are going to spend an average of $100 yearly.
So, your target market is around 1 million users.
2. Use TAM to find your Total Addressable Market
Once you have your target market, you need to find how much money they spend annually on products similar to yours. Or, if you have an active business, gather the average revenue you get per customer.
Using the equation we mentioned above, you simply multiply the total target market with the average revenue per customer. This is how you’ll find your TAM.
With the course example, that’s 1 million multiplied by $100, bringing the TAM to $100 million. Obviously, this isn’t the best of TAMs, but these are just sample numbers, and we’ve narrowed the TAM down quite a bit.
3. Use SAM to refine to the Serviceable Market for your product
Once you have your TAM, it’s time to find your SAM. You can simply do this by gauging what percentage of your total potential market you can optimally service with your product. Find what sub-niche your products speak to, and that’s the percentage of the total market you address.
So, for instance, you might only want to create a productivity course. Of the 1 million potential users, only 10% (100,000 users) might be in the market for your course. When you multiply that by the average $100 they spend on courses yearly, you get a SAM of $10 million. As you see, this is actually 10% of your TAM.
4. Use SOM to discover your Potential Market Share
Now, you need to find your SOM. Since SOM is basically a narrowed-down version of SAM, try to exclude potential customers who won’t be as profitable for your business. Maybe the age range you chose has a specific sub-range that spends less, or the ones who want a specific product also do a particular job.
Plus, you’ll need to take note of the competition within your niche and narrow down the SOM even further. In essence, you’re trying to find your market share. Once you have that, figure out how much the SAM will increase next year, multiply the number by your market share, and you’ve found your SOM.
Going back to our course example, maybe you don’t want to address the 18-24 range as much, as they spend a bit less than $100 per year. Or, you want to only address 25-35 who are actively working and want to be more productive at their work and in their life.
That leaves you with 40% market share, so 40,000 users. But you’re going up against 4 more creators in the niche, so you get only 20% of that (8,000 users) or 8% of the serviceable addressable market share of last year. If SAM increases by 10% year-over-year, that means that it goes up to $11 million, bringing your SOM to $880,000.
5. Outline your opportunities and challenges
With your SOM in mind, you now have a great idea of your revenue goals for this year or next year. This will help you find opportunities to pivot, like opening up to extra demographics and locations or offering new products and services.
You can also identify potential challenges. Maybe there’s a decline in your specific market, and so you won’t be able to hit the designated SOM. That helps you refocus your marketing and/or operations so that you can come as close to the SOM as possible.
Why TAM SAM SOM is important for business owners
Now, there’s no doubt that TAM SAM SOM is important. We wouldn’t have gone as in-depth into just 9 letters if they weren’t. Here are some areas where TAM SAM SOM can help you.
Market growth potential
By knowing your TAM and SAM, you can gauge how much potential your market has. When you’re starting a new business, that can help you understand if your idea is worth the time and resources to implement it or not. If you have an active business, it can help you spot potential pivoting opportunities to capture as much of the SAM as possible.
Resource allocation and budgeting
As for the SOM, it’s a clear metric to help you with your resource allocation and budgeting. If you notice that your marketing share is lower than expected and you’ve spent a large budget on it, you can refocus your marketing to more organic methods, like social media or SEO.
Speaking of budgeting, when you have a large SOM and a rather low cost, you can double down on your marketing and try to maximize the number of customers you have. The same goes vice versa (high product cost means more focus on improving your product rather than getting returning clients).
Investors
This one’s for all the startups. Investors will often judge startup ideas based on the TAM. A very large TAM ($1+ billion) means more competition, and so they might be reluctant to invest. A low TAM (less than $10 million) usually means that there aren’t too many growth opportunities, so it might not call for a large investment round.
Find more business advice and education on Whop
TAM SAM SOM is just one of the many tools businesses can use to find growth opportunities. There are, however, plenty more tips you can implement to scale your business that we didn’t cover. To learn these, you can join some of the many business and ecommerce whops.
These communities are hosted by industry leaders who have successfully scaled their businesses and are providing their knowledge to their members.
Many of these are also full of business owners, like you, who are in search of business advice and want to actively find ways to improve their business operations.
If you’re ready to join these servers, check out the Whop Marketplace. You’ll find hundreds of servers offering business advice across different industries, from ecom to digital services and everything in between.