We break down the top 25 ecommerce KPIs that will give you the insights you need to make smarter, more profitable data-driven decisions to elevate your business to new heights.
Key takeaways
- Align KPIs with specific business goals and limit tracking to a few actionable metrics to avoid information overload.
- Focus on KPIs that reveal actionable insights, like CAC and CLV, rather than vanity metrics without context.
- Regularly review and adjust your KPIs as business priorities shift from acquisition to retention or growth.
In ecommerce, to stay ahead of the competition you need more than a good product, you need to know that everything is optimized and which areas of your business need improvement.
That’s where key performance indicators (KPIs) come in. These metrics help you measure progress, optimize strategies, and keep your brand aligned with its goals.
In this article, we’ll break down the top 25 ecommerce KPIs that will give you the insights you need to make smarter, more profitable data-driven decisions to elevate your business to new heights. Keep reading and discover the best ecommerce KPIs you should track for success.
What are KPIs?
KPIs are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively a company or organization is achieving its key business objectives. KPIs help businesses track progress towards specific goals, identify areas of improvement, and make data-driven decisions.
In the context of ecommerce, KPIs are vital for understanding the success of marketing efforts, sales strategies, customer satisfaction, and overall business performance. Here are some of the common KPIs categories used in various aspects of a business:
- Sales KPIs: Measuring indicators like Revenue Growth, Conversion Rate (CVR), and Average Order Value (AOV).
- Marketing KPIs: Measuring indicators like Return on Ad Spend (ROAS), Marketing Efficiency Ratio (MER), and Email Open Rate.
- Customer Service KPIs: With indicators like Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), and Customer Retention Rate (CRR).
- Financial KPIs: Measuring Gross Profit Margin, Net Profit Margin, and Return on Investment (ROI).
- Operational KPIs: measuring indicators Inventory Turnover Rate, Order Fulfillment Time, and Return Rate.
How to choose the right KPIs to track
Choosing the right KPIs is crucial for accurately measuring the performance of your business and achieving your goals.
Here’s how you can choose KPIs that will provide the most value for your company.
Align KPIs with your business goals
Start by clearly defining your business objectives.
Are you focused on increasing revenue, improving customer retention, reducing costs, or expanding into new markets? Your KPIs should directly measure progress toward these specific goals.
If your goal is to boost sales, for example, you might focus on KPIs like Conversion Rate (CVR), Average Order Value (AOV), and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
Focus on actionable measurements
Good KPIs should help you identify trends and guide decision-making that leads to measurable improvements. So choose KPIs that give you insights into areas where you can take action.
A metric like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), for example, allows you to refine your marketing strategies to lower costs, whereas tracking something vague like “website visits” without context may not offer actionable insights.
Keep KPIs relevant to your industry
KPIs should reflect the unique aspects of your business and industry. In ecommerce, metrics like Cart Abandonment are far more relevant than they would be in a brick-and-mortar store, for example.
Other types of online business, like subscription-based communities, should track KPIs like Churn Rate, while online retailers might focus more on Inventory Turnover Rate, and Average Order Value (AOV).
Limit the number of KPIs
Tracking too many KPIs at once can lead to information overload and distract from what really matters for your business. So focus on a few key indicators that provide optimized insights. Depending on your type of business.
Review and adjust your KPIs regularly
Your KPIs should evolve as your business grows. Regularly assess whether the KPIs you’re tracking are still relevant and driving results. If your business shifts focus on the way, adjust or replace any KPIs that no longer align with your business goals.
For example, if your current marketing strategy shifts from acquisition to retention, KPIs like Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) might become more relevant for your business than Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). The number of KPIs already being tracked can influence this as well.
Ecommerce KPIs: The top 25 your business should be tracking
Here are the top 25 ecommerce KPis you should track for the success of your business:
1. Conversion Rate (CVR)
CRV measures the percentage of visitors to your website who complete action, like making a purchase. It’s one of the main KPIs for any ecommerce business to measure because it represents how a platform and its content are converting traffic into actual sales.
A low conversion rate may indicate a poor user experience, confusing navigation, or a disconnect between marketing efforts and what visitors expect.
- Utility: Tracking CVR helps ecommerce brands understand whether their website and marketing strategies are effective at driving sales. Improving CVR typically leads to increased revenue without the need for more traffic, making it a cost-effective area of optimization.
- Formula: Conversion Rate is calculated by dividing the total number of conversions (e.g., completed purchases) by the total number of visitors, then multiplying the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Read this guide if you're looking to improve your ecommerce conversion rate.
2. Average Order Value (AOV)
Represents the average amount of money a customer spends each time they place an order on an online store. This makes AOV essential for understanding how much revenue each specific transaction is generating.
- Utility: It helps businesses understand the buying behavior of their customers and can be used to inform pricing strategies, product bundling, and upsell opportunities.
- Formula: To calculate AOV, divide the total revenue by the number of orders placed during a specific period.
3. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
This is the total revenue a business can expect from a single customer throughout its commercial relationship. CLV takes into account the first purchase along with all subsequent purchases a customer makes over time. It’s an indicator, especially for businesses focusing on strategies for long-term growth.
- Utility: With CLV, businesses can make informed decisions about how much to invest in customer acquisition and retention strategies. A high CLV suggests customers are valuable over the long term, justifying higher Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC).
- Formula: Multiply the average purchase value by the purchase frequency and then by the average customer lifespan.
Learn more about customer lifetime value and why is it so important for business success.
4. Cart Abandonment Rate
The Cart Abandonment Rate is the percentage of customers who add items to their online shopping cart but leave the sales platform without completing the purchase. It’s an important metric for identifying barriers in the checkout process or points of friction that are causing potential customers to leave without converting.
- Utility: This metric helps sellers pinpoint areas where they are losing potential sales and offers insights into how the checkout process can be streamlined.
- Formula: To calculate the cart abandonment rate, subtract the number of completed purchases from the total number of shopping carts created, then divide this number by the total number of carts created. Multiply by 100 to express the result as a percentage.
5. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
The CAC measures how much your business spends trying to acquire new customers. This includes costs with marketing (hiring professionals, creating marketing material), advertising (paid ads and que costs of producing those ads), and sales expenses (every cost related to the product you’re selling), making it a crucial KPI for understanding the efficiency of your acquisition efforts.
- Utility: CAC helps businesses determine whether their marketing efforts are cost-effective.
- Formula: CAC is calculated by dividing the total marketing and sales costs by the number of new customers acquired over a given period.
6. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
For businesses focused on paid traffic strategies, ROAS evaluates the revenue generated from advertising compared to the cost of those ads. Studying this metric can show you if your ad spend is efficient and results in meaningful returns, or if your ads are underperforming and making your business lose money.
- Utility: Allows businesses to allocate budget accordingly to what performs best and adjust campaigns that aren’t delivering strong returns.
- Formula: You can calculate your ROAS by dividing the total revenue generated from ads by the total cost of the ads.
7. Marketing Efficiency Ratio (MER)
Marketing Efficiency Ratio measures the efficiency of your marketing campaign or strategy in terms of converting costs into actual profits. It’s commonly compared to ROAS, but the difference is that the marketing efficiency ratio focuses on overall campaign efficiency, while return on ad spend focuses on profitability per dollar spent on advertising.
- Utility: Especially useful for businesses with focused marketing teams, giving a view of how well the general marketing strategies are translating into profits.
- Formula: To calculate MER, divide the total revenue by the total marketing spend.
8. Bounce Rate
The Bounce Rate represents the percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only a single page. It’s an important metric for ecommerce businesses because a high bounce rate often signals that the content—or the overall user experience— of their sales channel is failing to engage visitors enough to make them stay on the page and explore further.
- Utility: Bounce Rate helps ecommerce businesses and even web designers, indicating problems with site speed, poor navigation, or other issues with websites.
- Formula: Bounce Rate is calculated by dividing the number of single-page sessions by the total number of sessions, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
9. Return Rate
While the possibility of product returns is an inevitable factor in ecommerce, this factor may signal issues like a lack of product quality, misleading descriptions, or even poor customer satisfaction. So this KPI represents the percentage of products that are returned after they are purchased.
- Utility: It serves as an important indicator of product quality and customer satisfaction in ecommerce.
- Formula: Return Rate is calculated by dividing the number of returned products by the total number of products sold, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
10. Gross Profit Margin
This KPI indicates how efficiently a company is producing and selling its products by measuring the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of the items sold. The higher the gross profit margin, the more profitable the company’s core business activities are.
- Utility: Is essential for understanding the overall profitability of your product offerings.
- Formula: Gross Profit Margin is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue, dividing that number by total revenue, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage.
11. Repeat Purchase Rate (RPR)
Repeat Purchase Rate is a specific KPI for understanding customer loyalty and satisfaction with your products and services by measuring the percentage of customers who return to make additional purchases (known as “repeat purchases”) after their first one.
- Utility: Repeat customers are often more profitable, so this can be an important KPI to track, especially if you plan to work on customer retention strategies.
- Formula: Repeat Purchase Rate is calculated by dividing the number of returning customers by the total number of customers, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
12. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Net Promoter Score indicates customer satisfaction and loyalty, and it’s based on single-question surveys to determine how likely customers are to recommend your business to others. For example, “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a colleague?".
Based on that question, customers are usually classified as Promoters (when answering 9 or 10), Passives (when answering 7 or 8), or Detractors (when answering between 0 and 6).
- Utility: NPS is a useful metric to predict future growth, as loyal customers tend to spend more and refer others.
- Formula: NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters. The result is a score ranging from -100 to 100.
13. Customer Retention Rate (CRR)
A high CRR is a strong indicator of customer loyalty and satisfaction, as this KPI measures the percentage of customers who continue to purchase from your store over a specific time, rather than switching to competitors or simply stopping buying from you.
- Utility: Gives insights into the quality of your products and customer service.
- Formula: Calculated by subtracting the number of new customers acquired during a specific period from the number of total customers at the end of that same period, then dividing the result by the number of customers at the beginning of the period.
Selling SaaS? Read more about customer retention metrics and why they matter.
14. Time to Purchase
Time to purchase is the average amount of time a customer takes to make a purchase after first arriving on your website. Tracking this KPI gives you insights into consumer behavior and how well your sales platform is operating in terms of speed and functionality.
- Utility: Businesses can identify and address friction points in the buyer’s journey, increasing conversions and creating a more seamless shopping experience.
- Formula: Time to Purchase is typically tracked using analytics software that records the time between a visitor’s first session and the moment they make a purchase.
15. Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score
Similar to the net promoter score, CSAT is typically gathered through post-purchase surveys that ask customers to rate their satisfaction on a numerical scale. But instead of focusing on the recommendations, the customer satisfaction score (as the name suggests) is focused solely on gathering customer satisfaction info.
- Utility: Helps businesses keep a pulse on customer happiness and identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Formula: To calculate CSAT, divide the number of satisfied customers by the total number of respondents, then multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
Learn how to keep your customers happy.
16. Churn Rate
This KPI is particularly important for subscription-based ecommerce models, like paid communities, and B2B companies overall. It shows the percentage of cancellations recorded in your customer base over time.
- Utility: Highlights customer loss and can help businesses identify and rectify underlying issues in their product or customer service.
- Formula: Churn Rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers lost during a specific period by the total number of customers at the start of that period, then multiplying by 100 to express it as a percentage.
For more detail read our full guide to Churn Rate.
17. Revenue Per Visitor (RPV)
RPV offers a clear picture of how much each visitor contributes to the profitability of your online platform by tracking the total amount of revenue generated from each visitor to your ecommerce website.
- Utility: Helps brands understand how effectively they are monetizing traffic.
- Formula: Revenue Per Visitor is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the total number of visitors.
18. Order Frequency
Order Frequency measures the average number of orders placed by a customer within a specified period of time.
- Utility: It reflects how often your customers are returning to your online store, being a clear measurement of customer loyalty.
- Formula: Order Frequency is calculated by dividing the total number of orders by the total number of unique customers over a specific period.
19. Email Open Rate
This specific KPI measures the percentage of recipients who open an email from an email marketing campaign.
- Utility: Gives you insights into whether your email strategy is resonating with your audience or not.
- Formula: Divide the number of opened emails by the number of emails sent (excluding bounces) and multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
20. Email Click-Through Rate (CTR)
This KPI dives even deeper into email analytics by measuring the percentage of email recipients who clicked on a link within your email (such as CTA buttons or hyperlinks) that led them to your landing page or website.
- Utility: It's one of the key indicators for determining the effectiveness of email marketing campaigns.
- Formula: CTR is calculated by dividing the number of email recipients who clicked on a link by the total number of emails delivered.
21. Cost Per Click (CPC)
Cost Per Click (CPC) measures the cost you pay for each click in your advertising campaign through Google Ads and Social Media Ads.
- Utility: Make advertising efforts more efficient by helping with budget management in paid advertising, maximizing traffic while minimizing costs,
- Formula: CPC is calculated by dividing the total cost of your PPC campaign by the total number of clicks.
22. Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
CPA measures how much it costs to acquire a customer through a specific campaign, allowing businesses to evaluate the performance of individual marketing campaigns and adjust their budgets accordingly.
- Utility: A lower CPA means your marketing dollars are being spent more efficiently to drive conversions.
- Formula: CPA is calculated by dividing the total campaign cost by the number of conversions (or acquisitions) that resulted from the campaign.
23. Inventory Turnover Rate
This shows how often a business sells and replaces its inventory within a certain period, typically annually. A high turnover rate indicates that products are selling quickly, while a low turnover rate may suggest excess inventory, slow sales, or misaligned stock levels.
- Utility: Helps businesses optimize their inventory management by ensuring they are neither overstocking nor understocking products.
- Formula: Inventory Turnover Rate is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory during a specific period.
24. Revenue Growth Rate
Revenue Growth Rate measures the rate at which a company’s revenue is increasing over a certain period. Rapid growth can signal that the business is scaling effectively, while stagnating or negative growth may indicate problems with the product or service, customer acquisition, or market conditions.
- Utility: Tracking Revenue Growth Rate helps businesses measure progress toward their financial goals and can inform strategic decisions.
- Formula: Revenue Growth Rate is calculated by subtracting the revenue of the previous period from the current period’s revenue, then dividing it by the previous period’s revenue. Multiply by 100 to express it as a percentage.
25. Customer Engagement Rate
This KPI tracks how actively customers interact with your brand across various touchpoints, such as social media, email, and on-site behavior.
- Utility: It goes beyond just purchases to understand how involved customers are with your brand, including likes, shares, comments, and other forms of interaction.
- Formula: Customer Engagement Rate can vary depending on the platform. For social media, it’s calculated by dividing total engagements (likes, comments, shares, etc.) by total followers, then multiplying by 100. For email, it might involve metrics like email open rate and click-through rate.
KPIs vs. metrics: What's the difference?

While KPIs and metrics are often used interchangeably (the word “metric” can even be used to identify a KPI like we used many times in this article) in ecommerce both are actually distinct terms with some differences.
In short, KPIs are indicators defined by managers to analyze the performance and results of a business, while metrics are raw information that can be used as a basis for KPIs.
But to fully understand the differences between KPIs and metrics, let’s take a look at their respective roles in areas like:
Strategic importance
KPIs focus on critical success factors aligned with your business goals.
Metrics provides data points about various aspects of your operations but may not directly affect marketing strategic objectives.
Actionable insights
KPIs offer clear insights that help guide high-level decision-making and strategy.
Metrics supplies general information that helps you monitor performance, but it doesn’t always drive immediate action.
Goal-oriented strategies
KPIs are always tied to achieving a specific goal (e.g., increasing revenue, or improving customer retention).
Metrics measure processes or activities without always being tied to a broader business objective.
Scope and focus
KPIs are valuables that narrowly focus on measuring success against critical business outcomes, mostly on a specific level.
Metrics are valuables that cover a wide range of activities, from user interactions to system efficiency, without being tied to the overall strategy.
Frequency of use
KPIs are usually tracked and reviewed regularly by leadership of companies or individual business owners to assess progress towards high-level goals.
Metrics are often tracked in day-to-day operations by specific teams, providing operational insights into operations
Why Whop is the best place for ecommerce business success
Are you starting a business, or need a helping hand to take your venture to the next level? Whop is a community full of experts ready to give you powerful insights into the world of ecommerce.
From courses on dropshipping to guides on how to make money from sports betting, and even creating and monetizing your own digital products, Whop has everything for every type of entrepreneur and it only takes a few clicks to get access.
Want to learn how to really make money in the ecommerce world?
Alternatively, if it's digital products or services that you're selling, why not sell them with Whop? Whop is an all-in-one platform with which you can sell everything from ebooks, to online community access, to online courses, coaching services, templates, and more.
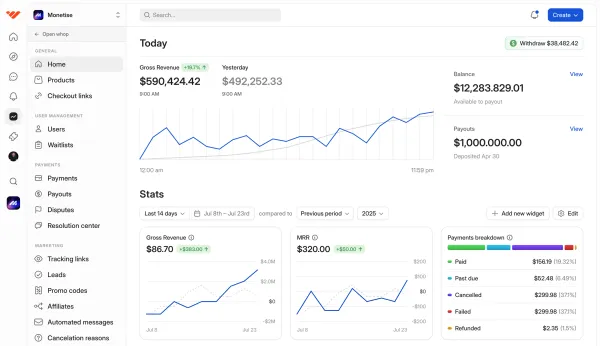
When you sell with Whop you not only get a customizable internet hub - aka your whop - but you also get access to a powerful seller dashboard.
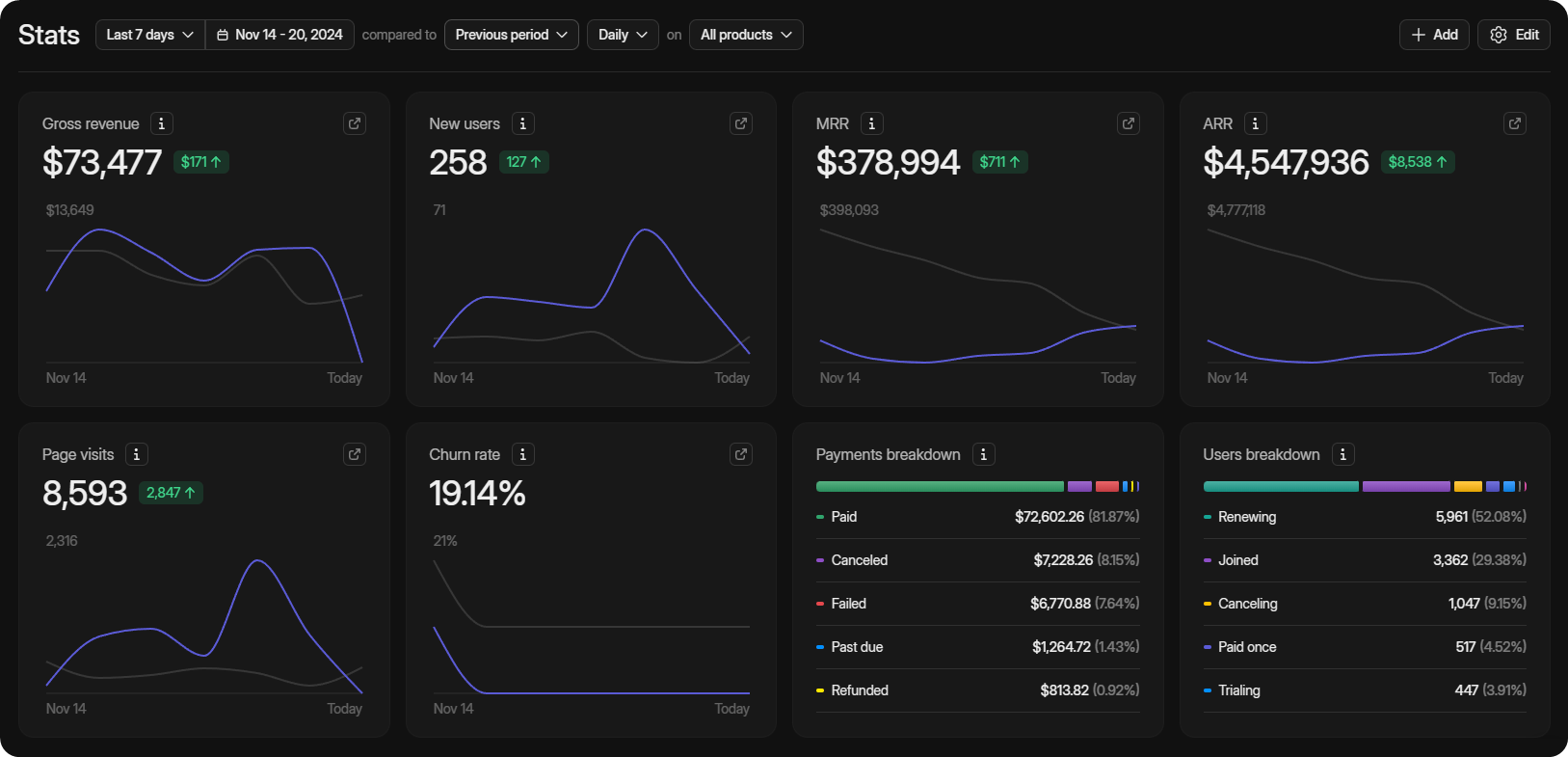
With your dashboard you can keep an eye on those all-important KPIs, including:
- Gross revenue
- New users
- Monthly Recurring Revenue
- Annual Recurring Revenue
- Page visits
- Churn Rate
- Payment breakdown
- User breakdown
Start selling with Whop and use these metrics and KPIs to power the growth of your online business.
Top ecommerce KPIs FAQs
The frequently asked questions about the top ecommerce KPIs.
What are ecommerce KPIs and why are they important?
KPIs are measurable metrics that help you track the performance of your online store in key areas like sales, customer behavior, and marketing. Tracking the right KPIs is crucial for optimizing revenue, improving customer retention, and ensuring overall business success.
Why you should trust Us
An ecommerce expert and senior content writer at Whop, Joe Niehaus brings years of expertise in ecommerce business and marketing solutions. His knowledge has also been highlighted in renowned outlets such as Business Insider, GQ, and Travel + Leisure.